- 12 - 16 JULY 2025
Cadaver dissection masterclass & education week
- ASAP Training Centre 15/F, Kailey Tower, 16 Stanley Street, Central Hong Kong
Organised By

Powered by
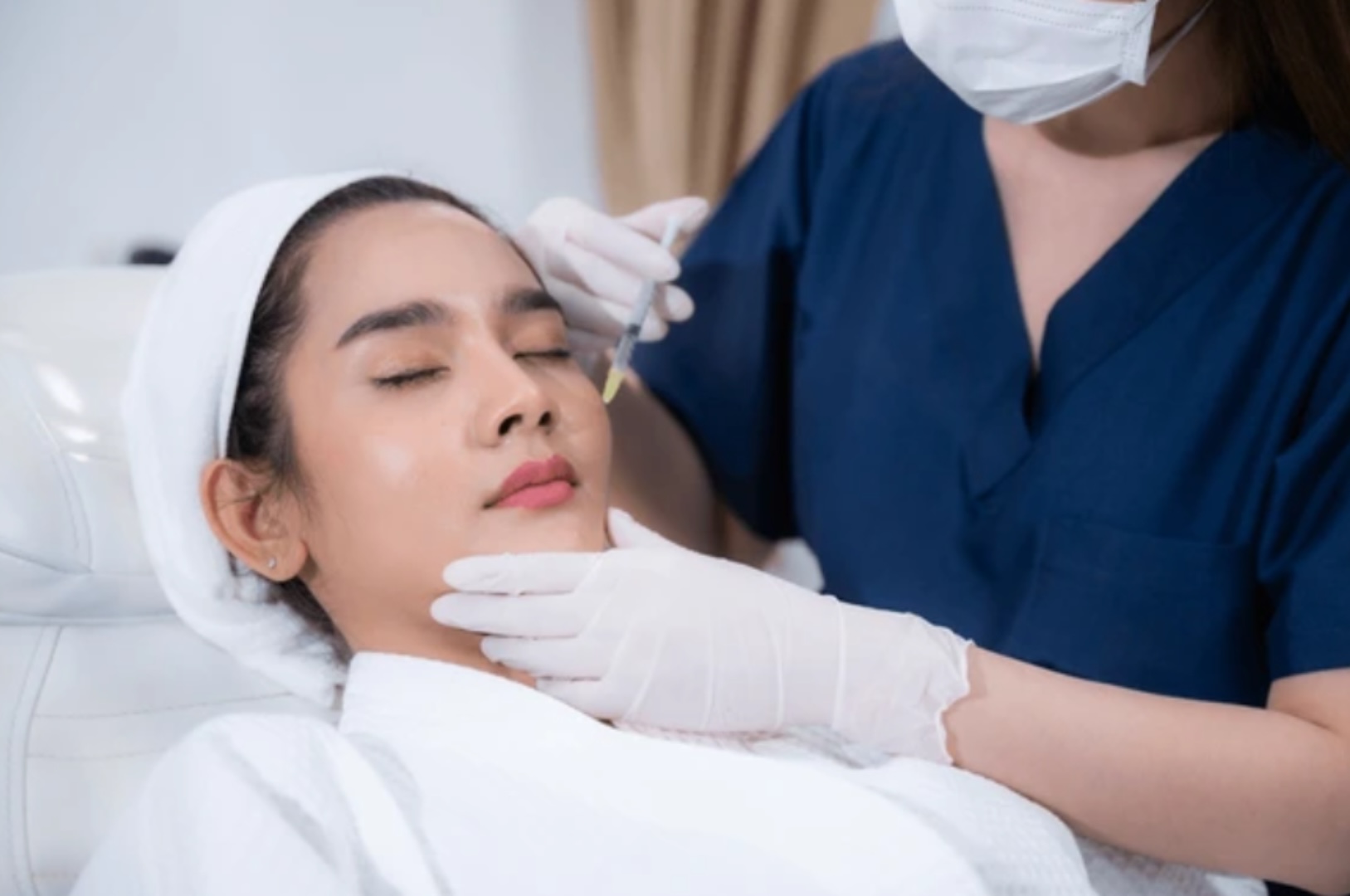

Cadaver hands-on masterclass for facial procedures
12 July 2025
Hong Kong University Cadaver Lab
Address : 10/F., Laboratory Block, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, 21 Sassoon Road, Pokfulam, Hong Kong
Agenda
Time
Program
08:00
Registration
08:30
Injection Practice
- Supraorbital ridge & deep temporal fossa periosteal filler injection
- Cannula filler injection
- Glabellar region Botox injection
09:30
Forehead Dissection
- Skin from frontalis
- Frontalis from forehead fat down to supra-orbital ridge
- Delineate glabella complex
- Supra-trochlear and supra-orbital foramina
10:30
Temporal Dissection
- Skin and subcutaneous fat
- Superficial temporal fascia (STF)
- Deep temporal fascia (DTF)
- Deep temporal fat pad
- Temporalis muscle
- Periosteum and bone
12:00
Lunch Break
13:00
Nose Procedures
- Nose filler injection
- Nose thread insertion
- Tear trough injection via cannula
14:00
Nose Dissection
- Skin drape via rhinoplasty approach
- Exposure of cartilages
15:30
Mid-face Dissection
- Dissection from nasolabial fold to orbicularis oculi (OO)
17:30
Round up Session / Q&A / Certification to Participants / Photo taking session
18:00
The End
Participation Fee for Cadaver Dissection Masterclass

Non ASAP Member Pass
USD2,000.00
Education Week Course Content
- 14 JULY 2025

Advanced course for neurotoxin (Botulinum Toxin A) applications in aesthetic medicine
- 15 JULY 2025
Filler injection course
- 16 JULY 2025

Medical Statistic Clash Course
USG course for FUSE (Facial Ultrasonography Evaluation) & MUSE (Musculoskeletal Ultrasonography Evaluation)
- 14 JULY 2025
Advanced course for neurotoxin (Botulinum Toxin A) applications in aesthetic medicine

Learning Objectives
- Master advanced injection techniques for the forehead, peri-orbital, nasal, and neck areas.
- Understand intricate muscle interactions and anatomical variations to minimize complications.
- Apply evidence-based protocols for nuanced treatments (e.g., micro-dosing, combination therapies).
- Develop skills to manage adverse events and tailor treatments to patient-specific anatomy.
Course Structure
Section 1: Forehead Area
- Micro-Neurotoxin Techniques for Frontalis
- Definition and rationale for micro-dosing vs. standard dosing.
- Patient selection criteria for subtle vs. dramatic results.
- Anatomy Deep Dive
- Frontalis muscle architecture and its interplay with the glabellar complex (procerus, corrugators, depressor supercilii).
- Septal structures and vascular anatomy (supratrochlear/
supraorbital arteries) to avoid bruising.
- Hands-On Techniques
- Horizontal vs. vertical injection patterns.
- Avoiding brow ptosis and “frozen” appearance.
Section 2: Peri-Orbital Area
- Orbicularis Oculi (OO) Anatomy
- Differentiation of orbital (forceful closure) vs. palpebral (gentle closure) OO fibers.
- Relationships with brow elevators (frontalis) and depressors (corrugators).
- Advanced Injection Strategies
- Crow’s feet: Layered approaches for dynamic vs. static wrinkles.
- Brow elevation: Targeting the lateral OO and tail of the brow.
- Avoiding complications: Ectropion, diplopia, and asymmetric smile.
- Case Studies
- Managing post-treatment edema and addressing under/over-correction.
Section 3: Nasal Area
- Muscle Anatomy
- Intrinsic muscles (nasalis, depressor septi) vs. extrinsic muscles (levator labii superioris alaeque nasi).
- Impact of muscle contractions on nasal aesthetics (e.g., nostril flaring).
- Advanced Treatments
- Bunny Lines: Targeting the transverse nasalis while sparing the levators.
- Nostril Dilatation Correction: Balancing depressor septi and nasalis injections.
- Risk Mitigation
- Avoiding lip ptosis or nasal valve collapse.
Section 4: Neck Area
- Platysma Anatomy and Dynamics
- Platysmal bands, decussation patterns, and interactions with mentalis muscle.
- Cervical retaining ligaments and their clinical implications.
- Nefertiti Lift Modifications
- Enhancing jawline definition by targeting platysma-cervical fascia junctions.
- Adjusting doses for male vs. female patients.
- Complication Management
- Dysphagia prevention: Safe zones and depth guidelines.
- Addressing weak neckline or paradoxical banding.
- 15 JULY 2025
Filler Injection Course

Course Structure
1. Introduction & Pre-Procedure Essentials
- Safety protocols: Hygiene, emergency preparedness, and legal/ethical considerations.
- Patient assessment: Anatomy review, skin type analysis, and psychological evaluation.
- Documentation: Informed consent, pre/post-procedure photography, and marking techniques.
2. Introduction & Pre-Procedure Essentials
Mechanisms, Indications, and Product Selection:
- Hyaluronic Acid (HA): Rheology, cross-linking, and reversible vs. non-reversible fillers.
- Poly-Lactic Acid (PLLA/PDLLA): Biostimulation principles, longevity, and layering techniques.
- Calcium Hydroxylapatite (CaHA), Polycaprolactone (PCL): Structural support and collagen induction.
- Emerging options: PMMA, HAAP, and combination therapies (e.g., fillers + toxins).
3. advanced techniques
Anatomic Zones & Injection Strategies (Demonstration + Theory):
- Forehead: Supraperiosteal vs. subcutaneous approaches; avoiding vascular compromise.
- Temporal Zone: Volumization for hollowing; cannula use and safety margins.
- Tear Trough: Layering techniques, blending with midface, and avoiding Tyndall effect.
- Nasolabial Fold: Dynamic vs. static folds; differential product selection.
- Cheek/Pre-Auricular Area: 3D volumization, lifting effects, and avoiding overcorrection.
- Chin: Projection vs. contouring; balancing with jawline harmonization.
4. Complications: Prevention & Management
- Early Recognition:
Vascular occlusion (blanching, pain), hypersensitivity, nodules, and infection. - Emergency Protocols:
Hyaluronidase administration, aspiration techniques, and escalation pathways. - Case Simulations: Group exercises on complication scenarios.
5. OBSERVER practical session
- Structured Practice:
- Rotating stations for each facial zone (forehead, tear trough, chin, etc.).
- Cadaver models/synthetic skin (if available) for safe practice.
- Real-time feedback from instructors.
- 16 JULY 2025
Medical Statistic Clash Course

Course Objectives
- Understand fundamental statistical concepts applied to clinical decision-making.
- Interpret clinical trial data, diagnostic tests, and risk assessments.
- Critically appraise medical literature for biases and validity.
- Apply statistical tools to improve patient outcomes and research quality.
Course Structure
1. Introduction to Statistical Medicine
- Role of statistics in clinical practice and research.
- Introduction to Population vs. sample, variables (continuous/categorical), hypothesis testing.
- Overview of Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines.
2. Study Design & Data Types
- Overviews of common types of clinical studies: RCTs, cohort, case-control, case series, cross-sectional.
- Bias and confounding: Selection bias, recall bias, confounding variables.
- Understand the common Data types: Nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio.
3. Sample Size & Power Analysis
- Calculating sample size for clinical trials.
- Power analysis: Avoiding underpowered studies.
- Tools: G-Power, online calculators.
4. Hypothesis Testing & Confidence Intervals
- Null vs. alternative hypotheses, p-values, Type I/II errors.
- Common tests: t-test, chi-square, ANOVA.
- Confidence intervals: Interpretation and clinical relevance.
5. Ethical & Practical Applications
- Data integrity: Handling missing data, outliers.
- Ethical considerations: Informed consent, data anonymization.
- Reporting standards: STROBE, PRISMA.
- Role of Ethic Committee (RED and IRB)
- 16 JULY 2025
USG course for FUSE (Facial Ultrasonography Evaluation) & MUSE (Musculoskeletal Ultrasonography Evaluation)
The Basics
- Basic ultrasound physics and anatomy with schematic explanation
- USG setting and operation mastering
- USG view correlation for anatomy
- The importance of FUSE
FUSE
1. FOREHEAD MODULE
1.1 Glabellar zone
- Supratrochlear NVB > Supraorbital NVB > Glabellar complex
1.2 Temporal zone
- Layers of the temporal zones > Superifical temporal artery
- Deep temporal arteries (anterior and posterior)
- Concept of Pitanguy line and implications
1.3 Use of vein viewer and USG
1.4 Complications of insultation to related vascular and neurological structures
2. MID-FACE MODULES
2.1 Zygoma and maxillary zone
- Mid-face land tear trough layers > Lip levator muscles
- Infra-orbital neurovascular bundle > Transverse facial artery and veins
2.2 Nasolabial fold
- Angular artery > Labial arteries > General idea of distal facial nerves
2.3 Nose region
- Infra-trohclear Artery and dorsal nasal artery
- Cartilage structures and anatomy > HA and prosthesis in situ
3. LOWER FACE MODULES
3.1 Facial artery
3.2 Mental foreman and NVB
3.3 Hypoglassal nerve and mental nerve
3.4 Submandibular/Parotid gland and neurotoxin
MUSE
4. Trapezius muscle
4.1 Anatomy and position
4.2 Important surrounding structure correlation
4.3 Approach of injection
5. Gastrocsoleus muscle
5.1 Anatomy and position
5.2 Important surrounding structure correlation
5.3 Approach of injection
Participation Fee for Education Week

Non ASAP Member Pass
HKD2,000.00 / course
To enjoy special rate at only HKD1,000.00/day/course for ASAP’s education week, you may also register as Delegate in AMSC Malaysia or AMSC Asia (in Hong Kong)
Register to attend AMSC Malaysia – www.amsc.com.my
Register to attend AMSC Asia (Hong Kong) – www.amsc.com.hk

Quick Link
About AMSC
Allied Health Society for Asia Pacific
E: garychai@thedeltus.com
M: +6016 538 9292
Secretariat
M: +852 61880835
A: 7/F, Kailey Tower, 16 Stanley Street, Central, Hong Kong
